Pavel Durov Can Travel As Some New Features Dribble from the Core Engineers
November 25, 2025
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
In November 2025, Telegram announced Cocoon, its AI system. Well, it is not yet revolutionizing writing code for smart contracts. Like Apple, Telegram is a bit late to the AI dog race. But there is hope for the company which has faced some headwinds. One blowing from the west is the criminal trial for which Pavel Durov, the founder of Telegram waits. Plus, the value of the much-hyped TONcoin and the subject of yet another investigation for financial fancy dancing is tanking.
What’s the good news? Telegram watching outfits like FoneArena and PCNews.ru have reported on some recent Telegram innovations. Keep in mind that Telegram means that a new user install the Messenger mini app. This is an “everything” app. Through the interface one can do a wide range of actions. Yep, that’s why it is called an “everything” app. You can read Telegram’s own explanation in the firm’s blog.
Fone Arena reports that “the Dubai-based virtual company (yeah, go figure that out) has rolled out Live Stories streaming, repeated messages, and gift auctions. Repeated messages will spark some bot developers to build this function into applications. Notifications (wanted and unwanted) are useful in certain types of advertising campaigns. The gift auctions is little more than a hybrid of Google ad auctions and eBay applied to the highly volatile, speculative crypto confections Telegram, users, and developers allegedly find of great value.
The Live Stories streaming is more significant. Rolled out in November 2025, Live Stories allows users to broadcast live streams within the Stories service. Viewers can post comments and interact in real time in a live chat. During a stream, viewers may highlight or pin their messages using Telegram Stars, which is a form of crypto cash. A visible Star counter appears in the corner of the broadcast. Gamification is a big part of the Telegram way. Gambling means crypto transactions. Transactions incur a service charge. A user can kick of a Live Story from a personal accounts or from a Groups or a Channels that have unlocked Story posting via boosts. Owners have to unlock the Live Story, however. Plus, the new service supports real time messaging protocol for external applications such as OBS and XSplit streaming software.
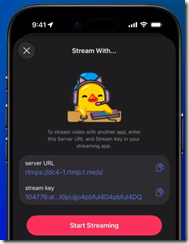
The interface for Live Stories steaming. Is Telegram angling to kill off Twitch and put a dent in Discord? Will the French judiciary forget to try Pavel Durov for his online service’s behavior. It appears that Mr. Durov and his core engineers think so.
Observations are warranted:
- Live Stories is likely to catch the attention of some of the more interesting crypto promoters who make use of Telegram
- Telegram’s monitoring service will have to operate in real time because dropping in a short but interesting video promo for certain illegal or controversial activities will have to operate better than the Cleveland Browns American football team
- The soft hooks to pump up service charges or “gas fees” in the lingo of the digital currency enthusiasts are an important part of gift and auction play. Think hooking users on speculative investments in digital goodies and then scraping off those service charges.
Net net: Will Cocoon make it easier for developers to code complex bots, mini apps, and distributed applications (dApps)? Answer: Not yet. Just go buy a gift on Telegram. PS. Mr. Zuckerberg, Telegram has aced you again it seems.
Stephen E Arnold, November 25, 2025
Watson: Transmission Is Doing Its Part
November 25, 2025
 Another dinobaby post. No AI unless it is an image. This dinobaby is not Grandma Moses, just Grandpa Arnold.
Another dinobaby post. No AI unless it is an image. This dinobaby is not Grandma Moses, just Grandpa Arnold.
I read an article that stopped me in my tracks. It was “IBM Revisits 2011 AI Jeopardy Win to Capture B2B Demand.” The article reports that a former IBM executive said:
People want AI to be able to do what it can’t…. and immature technology companies are not disciplined enough to correct that thinking.
I find the statement fascinating. IBM Watson was supposed to address some of the challenges cancer patients faced. The reality is that cancer docs in Houston and Manhattan provided IBM with some feedback that shattered IBM’s own ill-disciplined marketing of Watson. What about that building near NYU that was stuffed with AI experts? What about IBM’s sale of its medical unit to Francisco Partners? Where is that smart software today? It is Merative Health, and it is not clear if the company is hitting home runs and generating a flood of cash. So that Watson technology is no longer part of IBM’s smart software solution.

Thanks, Venice.ai. Good enough.
The write up reports that a company called Transmission, which is a business to business or B2B marketing agency, made a documentary about Watson AI. It is not clear from the write up if the documentary was sponsored or if Transmission just had the idea to revisit Watson. According to the write up:
The documentary [“Who is…Watson? The Day AI Went Primetime”] underscores IBM’s legacy of innovation while framing its role in shaping an ethical, inclusive future for AI, a critical differentiator in today’s competitive landscape.
The Transmission/Earnest documentary is a rah rah for IBM and its Watsonx technology. Think of this as Watson Version 2 or Version 3. The Transmission outfit and its Earnest unit (yes, that is its name) in London, England, wants to land more IBM work. Furthermore, rumors suggest that the video created by Celia Aniskovich as a “spec project.” High quality videos running 18 minutes can burn through six figures quickly. A cost of $250,000 or $300,000 is not unexpected. Add to this the cost of the PR campaign to push Transmission brand story telling capability, and the investment strikes me as a bad-economy sales move. If a fat economy, a marketing outfit would just book business at trade shows or lunch. Now, it is rah rah time and cash outflow.
The write up makes clear that Transmission put its best foot forward. I learned:
The documentary was grounded in testimonials from former IBM staff, and more B2B players are building narratives around expert commentary. B2B marketers say thought leaders and industry analysts are the most effective influencer types (28%), according to an April LinkedIn and Ipsos survey. AI pushback is a hot topic, and so is creating more entertaining B2B content. The biggest concern among leveraging AI tools among adults worldwide is the loss of human jobs, according to a May Kantar survey. The primary goal for video marketing is brand awareness (35%), according to an April LinkedIn and Ipsos survey. In an era where AI is perceived as “abstract or intimidating,” this documentary attempts to humanize it while embracing the narrative style that makes B2B brands stand out,
The IBM message is important. Watson Jeopardy was “good” AI. The move fast, break things, and spend billions approach used today is not like IBM’s approach to Watson. (Too bad about those cancer docs not embracing Watson, a factoid not mentioned in the cited write up.)
The question is. “Will the Watson video go viral?” The Watson Jeopardy dust up took place in 2011, but the Watson name lives on. Google is probably shaking its talons at the sky wishing it had a flashy video too. My hunch is that Google would let its AI make a video or one of the YouTubers would volunteer hoping that an act of goodness would reduce the likelihood Google would cut their YouTube payments. I guess I could ask Watson when it thinks, but I won’t. Been there. Done that.
Stephen E Arnold, November 25, 2025
Tim Apple, Granny Scarfs, and Snooping
November 24, 2025
 Another dinobaby post. No AI unless it is an image. This dinobaby is not Grandma Moses, just Grandpa Arnold.
Another dinobaby post. No AI unless it is an image. This dinobaby is not Grandma Moses, just Grandpa Arnold.
I spotted a write in a source I usually ignore. I don’t know if the write up is 100 percent on the money. Let’s assume for the purpose of my dinobaby persona that it indeed is. The write up is “Apple to Pay $95 Million Settle Suit Accusing Siri Of Snoopy Eavesdropping.” Like Apple’s incessant pop ups about my not logging into Facetime, iMessage, and iCloud, Siri being in snoop mode is not surprising to me. Tim Apple, it seems, is winding down. The pace of innovation, in my opinion, is tortoise like. I haven’t nothing against turtle like creatures, but a granny scarf for an iPhone. That’s innovation, almost as cutting edge as the candy colored orange iPhone. Stunning indeed.

Is Frederick the Great wearing an Apple Granny Scarf? Thanks, Venice.ai. Good enough.
What does the write up say about this $95 million sad smile?
Apple has agreed to pay $95 million to settle a lawsuit accusing the privacy-minded company of deploying its virtual assistant Siri to eavesdrop on people using its iPhone and other trendy devices. The proposed settlement filed Tuesday in an Oakland, California, federal court would resolve a 5-year-old lawsuit revolving around allegations that Apple surreptitiously activated Siri to record conversations through iPhones and other devices equipped with the virtual assistant for more than a decade.
Apple has managed to work the legal process for five years. Good work, legal eagles. Billable hours and legal moves generate income if my understanding is correct. Also, the notion of “surreptitiously” fascinates me. Why do the crazy screen nagging? Just activate what you want and remove the users’ options to disable the function. If you want to be surreptitious, the basic concept as I understand it is to operate so others don’t know what you are doing. Good try, but you failed to implement appropriate secretive operational methods. Better luck next time or just enable what you want and prevent users from turning off the data vacuum cleaner.
The write up notes:
Apple isn’t acknowledging any wrongdoing in the settlement, which still must be approved by U.S. District Judge Jeffrey White. Lawyers in the case have proposed scheduling a Feb. 14 court hearing in Oakland to review the terms.
I interpreted this passage to mean that the Judge has to do something. I assume that lawyers will do something. Whoever brought the litigation will do something. It strikes me that Apple will not be writing a check any time soon, nor will the fine change how Tim Apple has set up that outstanding Apple entity to harvest money, data, and good vibes.
I have several questions:
- Will Apple offer a complementary Granny Scarf to each of its attorneys working this case?
- Will Apple’s methods of harvesting data be revealed in a white paper written by either [a] Apple, [b] an unhappy Apple employee, or [c] a researcher laboring in the vineyards of Stanford University or San Jose State?
- Will regulatory authorities and the US judicial folks take steps to curtail the “we do what we want” approach to privacy and security?
I have answers for each of these questions. Here we go:
- No. Granny Scarfs are sold out
- No. No one wants to be hassled endlessly by Apple’s legions of legal eagles
- No. As the recent Meta decision about WhatsApp makes clear, green light, tech bros. Move fast, break things. Just do it.
Stephen E Arnold, November 24, 2025
Google: AI or Else. What a Pleasant, Implicit Threat
November 24, 2025
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Do you remember that old chestnut of a how-to book. I think its title was How to Win Friends and Influence People. I think the book contains a statement like this:
“Instead of condemning people, let’s try to understand them. Let’s try to figure out why they do what they do. That’s a lot more profitable and intriguing than criticism; and it breeds sympathy, tolerance and kindness. “To know all is to forgive all.” ”
The Google leadership has mastered this approach. Look at its successes. An advertising system that sells access to users from an automated bidding system running within the Google platform. Isn’t that a way to breed sympathy for the company’s approach to serving the needs of its customers? Another example is the brilliant idea of making a Google-centric Agentic Operating System for the world. I know that the approach leaves plenty of room for Google partners, Google high performers, and Google services. Won’t everyone respond in a positive way to the “space” that Google leaves for others?

Thanks, Venice.ai. Good enough.
I read “Google Boss Warns No Company Is Going to Be Immune If AI Bubble Bursts.” What an excellent example of putting the old-fashioned precepts of Dale Carnegie’s book into practice. The soon-to-be-sued BBC article states:
Speaking exclusively to BBC News, Sundar Pichai said while the growth of artificial intelligence (AI) investment had been an “extraordinary moment”, there was some “irrationality” in the current AI boom… “I think no company is going to be immune, including us,” he said.
My memory doesn’t work the way it did when I was 13 years old, but I think I heard this same Silicon Valley luminary say, “Code Red” when Microsoft announced a deal to put AI in its products and services. With the klaxon sounding and flashing warning lights, Google began pushing people and money into smart software. Thus, the AI craze was legitimized. Not even the spat between Sam Altman and Elon Musk could slow the acceleration. And where are we now?
The chief Googler, a former McKinsey & Company consultant, is explaining that the AI boom is rational and irrational. Is that a threat from a company that knee jerked its way forward? Is Google saying that I should embrace AI or suffer the consequences? Mr. Pichai is worried about the energy needs of AI. That’s good. Because one doesn’t need to be an expert in utility forecast demand analysis to figure out that if the announced data centers are built, there will probably be brown outs or power rationing. Companies like Google can pay its electric bills; others may not have the benefit of that outstanding advertising system to spit out cash with the heart beat of an atomic clock.
I am not sure that Dale Carnegie would have phrased statements like these if they are words tumbling from Google’s leader as presented in the article:
“We will have to work through societal disruptions.” he said, adding that it would also “create new opportunities”. “It will evolve and transition certain jobs, and people will need to adapt,” he said. Those who do adapt to AI “will do better”. “It doesn’t matter whether you want to be a teacher [or] a doctor. All those professions will be around, but the people who will do well in each of those professions are people who learn how to use these tools.”
This sure sounds like a dire prediction for people who don’t “learn how to use these tools.” I would go so far as to suggest that one of the progenitors of the AI craziness is making another threat. I interpret the comment as meaning, “Get with the program or you will never work again anywhere.”
How uplifting. Imagine that old coot Dale Carnegie saying in the 1930s that you will do poorly if you don’t get with the Googley AI program? Here’s one of Dale’s off-the-wall comments was:
“The only way to influence people is to talk in terms of what the other person wants.”
The statements in the BBC story make one thing clear: I know what Google wants. I am not sure it is what other people want. Obviously the wacko Dale Carnegie is not in tune with the McKinsey consultant’s pragmatic view of what Google wants. Poor Dale. It seems his observations do not line up with the Google view of life for those who don’t do AI.
Stephen E Arnold, November 24, 2025
Microsoft Factoid: 30 Percent of Our Code Is Vibey
November 24, 2025
 Another short essay from a real and still-alive dinobaby. If you see an image, we used AI. The dinobaby is not an artist like Grandma Moses.
Another short essay from a real and still-alive dinobaby. If you see an image, we used AI. The dinobaby is not an artist like Grandma Moses.
Is Microsoft cranking out one fifth to one third of its code using vibey methods? A write up from Ibrahim Diallo seeks to answer this question in his essay “Is 30% of Microsoft’s Code Really AI-Generated?” My instinctive response was, “Nope. Marketing.” Microsoft feels the heat. The Google is pushing the message that it will deliver the Agentic Operating System for the emergence of a new computing epoch. In response, Microsoft has been pumping juice into its market collateral. For example, Microsoft is building data center systems that span nations. Copilot will make your Notepad “experience” more memorable. Visio, a step child application, is really cheap. Add these steps together, and you get a profile of a very large company under pressure and showing signs of cracking. Why? Google is turning up the heat and Microsoft feels it.
Mr. Diallo writes:
A few months back, news outlets were buzzing with reports that Satya Nadella claimed 30% of the code in Microsoft’s repositories was AI-generated. This fueled the hype around tools like Copilot and Cursor. The implication seemed clear: if Microsoft’s developers were now “vibe coding,” everyone should embrace the method.
Then he makes a pragmatic observation:
The line between “AI-generated” and “human-written” code has become blurrier than the headlines suggest. And maybe that’s the point. When AI becomes just another tool in the development workflow, like syntax highlighting or auto-complete, measuring its contribution as a simple percentage might not be meaningful at all.
Several observations:
- Microsoft’s leadership is outputting difficult to believe statements
- Microsoft apparently has been recycling code because those contributions from Stack Overflow are not tabulated
- Marketing is now the engine making AI the future of Microsoft unfold.
I would assert that the answer to the Mr. Diallo’s question is, “Whatever unfounded assertion Microsoft offers is actual factual.” That’s okay with me, but some people may be hooked by Google’s Agentic Operating System pitch.
Stephen E Arnold, November 24, 2025
Collaboration: Why Ask? Just Do. (Great Advice, Job Seeker)
November 24, 2025
 Another short essay from a real and still-alive dinobaby. If you see an image, we used AI. The dinobaby is not an artist like Grandma Moses.
Another short essay from a real and still-alive dinobaby. If you see an image, we used AI. The dinobaby is not an artist like Grandma Moses.
I read
I am too old to have an opinion about collaboration in 2025. I am a slacker, not a user of Slack. I don’t “GoTo” meetings; I stay in my underground office. I don’t “chat” on Facebook or smart software. I am, therefore, qualified to comment on the essay “Collaboration Sucks.” The main point of the essay is that collaboration is not a positive. (I know that this person has not worked at a blue chip consulting firm. If you don’t collaborate, you better have telepathy. Otherwise, you will screw up in a spectacular fashion with the client and the lucky colleagues who get to write about your performance or just drop hints to a Carpetland dweller.
The essay states:
We aim to hire people who are great at their jobs and get out of their way. No deadlines, minimal coordination, and no managers telling you what to do. In return, we ask for extraordinarily high ownership and the ability to get a lot done by yourself. Marketers ship code, salespeople answer technical questions without backup, and product engineers work across the stack.
To me, this sounds like a Silicon Valley commandment along with “Go fast and break things” or “It’s easier to ask forgiveness than it is to get permission.” Allegedly Rear Admiral Grace Hopper offered this observation. However, Admiral Craig Hosmer told me that her attitude did more harm to females in the US Navy’s technical services than she thought. Which Admiral does one believe? I believe what Admiral Hosmer told me when I provided technical support to his little Joint Committee on Nuclear Energy many years ago.

Thanks, Venice.ai. Good enough. Good enough.
The idea that a team of really smart and independent specialists can do great things is what has made respected managers familiar with legal processes around the world. I think Google just received an opportunity to learn from its $600 million fine levied by Germany. Moving fast, Google made some interesting decisions about German price comparison sites. I won’t raise again the specter of the AI bubble and the leadership methods of Sam AI-Man. Everything is working out just swell, right?
The write up presents seven reasons why collaboration sucks. Most of the reasons revolve around flaws in a person. I urge you to read the seven variations on the theme of insecurity, impostor syndrome, and cluelessness.
My view is that collaboration, like any business process, depends on the context of the task and the work itself. In some organizations, employees can do almost anything because middle managers (if they are still present) have little idea about what’s going on with workers who are in an office half a world away, down the hall but playing Foosball, pecking away at a laptop in a small, overpriced apartment in Plastic Fantastic (aka San Mateo), or working from a van and hoping the Starlink is up.
I like the idea of crushing collaboration. I urge those who want to practice this skill join a big time law firm, a blue chip consulting firm, or engage in the work underway at a pharmaceutical research lab. I love the tips the author trots out; specifically:
- Just ship the code, product, whatever. Ignore inputs like Slack messages.
- Tell the boss or leader, you are the “driver.” (When I worked for the Admiral, I would suggest that this approach was not appropriate for the context of that professional, the work related to nuclear weapons, or a way to win his love, affection, and respect. I would urge the author to track down a four star and give his method a whirl. Let me know how that works out.)
- Tell people what you need. That’s a great idea if one has power and influence. If not, it is probably important to let ChatGPT word an email for you.
- Don’t give anyone feedback until the code or product has shipped. This a career builder in some organizations. It is quite relevant when a massive penalty ensures because an individual withheld knowledge and thus made the problem worse. (There is something called “discovery.” And, guess what, those Slack and email messages can be potent.)
- Listen to inputs but just do what you want. (In my 60 year work career, I am not sure this has ever been good advice. In an AI outfit, it’s probably gold for someone. Isn’t there something called Fool’s Gold?)
Plus, there is one item on the action list for crushing collaboration I did not understand. Maybe you can divine its meaning? “If you are a team lead, or leader of leads, who has been asked for feedback, consider being more you can just do stuff.”
Several observations:
- I am glad I am not working in Sillycon Valley any longer. I loved the commute from Berkeley each day, but the craziness in play today would not match my context. Translation: I have had enough of destructive business methods. Find someone else to do your work.
- The suggestions for killing collaboration may kill one’s career except in toxic companies. (Notice that I did not identify AI-centric outfits. How politic of me.)
- The management failure implicit in this approach to colleagues, suggestions, and striving for quality is obvious to me. My fear is that some young professionals may see this collaboration sucks approach and fail to recognize the issues it creates.
Net net: When you hire, I suggest you match the individual to the context and the expertise required to the job. Short cuts contribute to the high failure rate of start ups and the dead end careers some promising workers create for themselves.
Stephen E Arnold, November 24, 2025
AI Doubters: You Fall Short. Just Get With the Program
November 21, 2025
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Watching the Google strike terror in the heart of Sam AI-Man is almost as good as watching a mismatch in bare knuckle fights broadcast on free TV. Promoters have a person who appears fit and mean. The opponent usually looks less physically imposing and often has a neutral or slightly frightened expression. After a few minutes, the big person wins.
Is the current state of AI like a bare knuckles fight?
Here’s another example. A math whiz in a first year algebra class is asked by the teacher, “Why didn’t you show your work?” The young person looks confused and says, “The answer is obvious.” The teacher says you have to show your work. The 13-year old replies, “There is nothing to show. The answer just is.”

A young wizard has no use for an old fuddy duddy who wants to cling to the past. The future leadership gem thinks, “Dude, I am in Hilbert space.”
I thought that BAIT executives had outgrown or at least learned to mask their ability to pound the opponent to the canvas and figured out how to keep their innate superiority in check. Not surprisingly, I was wrong.
My awareness of the mismatch surfaced when I read “Microsoft AI CEO Puzzled by People Being Unimpressed by AI.” The hyperbole surrounding AI or smart software is the equivalent of the physically fit person pummeling an individual probably better suited to work as an insurance clerk into the emergency room. It makes clear that the whiz kid in math class has no clue that other people do not see what “just is.”
Let’s take a look at a couple of statements in the article.
I noted this allegedly accurate passage:
It cracks me up when I hear people call AI underwhelming. I grew up playing Snake on a Nokia phone! The fact that people are unimpressed that we can have a fluent conversation with a super smart AI that can generate any image/video is mind blowing to me.
What you haven’t fallen succumbed to the marketing punches yet? And you don’t get it? I can almost hear a voice saying, “Yep, you Mr. Dinobaby, are a loser.” The person saying “cracks me up” is the notable Mustafa Suleyman. He is Microsoft’s top dog in smart software. He is famous in AI circles. He did not understand this “show your work” stuff. He would be a very good bet in a bare knuckles contest is my guess.
A second snippet:
Over in the comments, some users pushed back on the CEO’s use of the word “unimpressed,” arguing that it’s not the technology itself that fails to impress them, but rather Microsoft’s tendency to put AI into everything just to appease shareholders instead of focusing on the issues that most users actually care about, like making Windows’ UI more user-friendly similar to how it was in Windows 7, fixing security problems, and taking user privacy more seriously.
The second snippet is a response to Mr. Suleyman’s bafflement. The idea that 40 year old Microsoft is reinventing itself with AI troubles the person who brings up Windows’ issues. SolarWinds is officially put to bed, pummeled by tough lawyers and the news cycle. The second snippet brings up an idea that strikes some as ludicrous; specifically, paying attention to what users want.
Several observations:
- Microsoft and other AI firms know what’s best for me and you
- The AI push is a somewhat overwrought attempt to make a particular technical system the next big thing. The idea is that if we say it and think it and fund it, AI will be like electricity, the Internet, and an iPhone.
- The money at stake means that those who do not understand the value of smart software are obstructionists. These individuals and organizations will have to withstand the force of the superior combatants.
Will AI beat those who just want software to assist them complete a task, not generate made up or incorrect outputs, and allow people to work in a way that is comfortable to them? My hunch is that users of software will have to get with the program. The algebra teacher will, one way or another, fail to contain the confidence, arrogance, and intelligence of the person who states, “It just is.”
Stephen E Arnold, November 21, 2025
AI Spending Killing Jobs, Not AI Technology
November 21, 2025
 Another short essay from a real and still-alive dinobaby. If you see an image, we used AI. The dinobaby is not an artist like Grandma Moses.
Another short essay from a real and still-alive dinobaby. If you see an image, we used AI. The dinobaby is not an artist like Grandma Moses.
Fast Company published “AI Isn’t Replacing Jobs. AI Spending Is.” The job losses are real. Reports from recruiting firms and anecdotal information make it clear that those over 55 are at risk and most of those under 23 are likely to be candidates for mom’s basement or van life.

Thanks, Venice.ai. Pretty lame, but I grew bored with trying different prompts.
The write up says:
From Amazon to General Motors to Booz Allen Hamilton, layoffs are being announced and blamed on AI. Amazon said it would cut 14,000 corporate jobs. United Parcel Service (UPS) said it had reduced its management workforce by about 14,000 positions over the past 22 months. And Target said it would cut 1,800 corporate roles. Some academic economists have also chimed in: The St. Louis Federal Reserve found a (weak) correlation between theoretical AI exposure and actual AI adoption in 12 occupational categories.
Then the article delivers an interesting point:
Yet we remain skeptical of the claim that AI is responsible for these layoffs. A recent MIT Media Lab study found that 95% of generative AI pilot business projects were failing. Another survey by Atlassian concluded that 96% of businesses “have not seen dramatic improvements in organizational efficiency, innovation, or work quality.” Still another study found that 40% of the business people surveyed have received “AI slop” at work in the last month and that it takes nearly two hours, on average, to fix each instance of slop. In addition, they “no longer trust their AI-enabled peers, find them less creative, and find them less intelligent or capable.”
Here’s the interesting conclusion or semi-assertion:
When companies are financially stressed, a relatively easy solution is to lay off workers and ask those who are not laid off to work harder and be thankful that they still have jobs. AI is just a convenient excuse for this cost-cutting.
Yep, AI spending is not producing revenue. The sheep herd is following AI. But fodder is expensive. Therefore, cull the sheep. Wool sweaters at a discount, anyone? Then the skepticism of a more or less traditional publishing outfit surfaces; to wit:
The wild exaggerations from LLM promoters certainly help them raise funds for their quixotic quest for artificial general intelligence. But it brings us no closer to that goal, all while diverting valuable physical, financial, and human resources from more promising pursuits.
Several observations are probably unnecessary, but I as an official dinobaby choose to offer them herewith:
- The next big thing that has been easy to juice has been AI. Is it the next big thing? Nope, it is utility software. Does anyone need multiple utility applications? Nope. Does anyone want multiple utility tools that do mostly the same thing with about the same amount of made up and incorrect outputs? Nope.
- The drivers for AI are easy to identify: [a] It was easy to hype, [b] People like the idea of a silver bullet until the bullets misfire and blow off the shooter’s hand or blind the gun lover, [c] No other “next big thing” is at hand.
- Incorrect investment decisions are more problematic than diversified investment decisions. What do oligopolistic outfits do? Lead their followers. If we think in terms of sheep, there are a lot of sheet facing a very steep cliff.
Net net: Only a couple of sheep will emerge as Big Sheep. The other sheep? Well, if not a sweater, how about a lamb chop. Ooops. Some sheep may not want to become food items on a Styrofoam tray wrapped in plastic with a half off price tag. Imagine that.
Stephen E Arnold, November 21, 2025
Waymo Mows Down a Mission Cat
November 21, 2025
Cat lovers in San Francisco have a new reason to be angry at Waymo, Google’s self-driving car division. The outrage has reached all the way to the UK, where the Metro reports, “Robotaxi Runs Over and Kills Popular Cat that Greeted People in a Corner Shop.” Reporter Sarah Hooper writes:
“KitKat, the beloved pet cat at Randa’s Market, was run over by an automated car on October 27. He was rushed to a hospital by a bartender working nearby, but was pronounced dead. KitKat’s death has sparked an outpouring of fury and sadness from those who loved him – and questions about the dangers posed by self-driving cars. Randa’s Market owner Mike Zeidan told Rolling Stone: ‘He was a special cat. You can tell by the love and support he’s getting from the community that he was amazing.’ San Francisco Supervisor Jackie Fielder spoke out publicly, saying: ‘Waymo thinks they can just sweep this under the rug and we will all forget, but here in the Mission, we will never forget our sweet KitKat.’ Anger in the community has increased after it was revealed that on the same day KitKat was killed, Waymo co-CEO Tekedra Mawakana said she thought society is ‘ready to accept deaths’ caused by automated cars. But KitKat’s owner pointed out that next time, the death could be that of a child, not just a beloved pet.”
Good point. In a statement, the company insists the tabby “darted” under the car as it pulled away. Perhaps. But do the big dogs at Google really feel “deepest sympathies” for those grieving their furry friend, as the statement claims? It was one of them, after all, who asserted the world is ready to trade deaths for her firm’s technology.
Curious readers can navigate to the write-up to see a couple photos of the charismatic kitty.
Cynthia Murrell, November 21, 2025
Data Centers: Going information Dark
November 21, 2025
Data Center NDAs: Keeping Citizens in the Dark Until the Ink is Dry
Transparency is a dirty word in Silicon Valley. And now, increasingly, across the country. NBC News discusses “How NDAs Keep AI Data Center Details Hidden from Americans.” Reporter Natalie Kainz tells us about Dr. Timothy Grosser of Mason County, Kentucky, who turned down a generous but mysterious offer to buy his 250-acre farm. Those who brought him the proposal refused to tell him who it came from or what the land would be used for. They asked him to sign a non-disclosure agreement before revealing such details. The farmer, who has no intention of selling his land to anyone for any price, adamantly refused. Later, he learned a still-unnamed company is scouting the area for a huge data center. Kainz writes:
“Grosser experienced firsthand what has become a common but controversial aspect of the multibillion-dollar data center boom, fueled by artificial intelligence services. Major tech companies launching the huge projects across the country are asking land sellers and public officials to sign NDAs to limit discussions about details of the projects in exchange for morsels of information and the potential of economic lifelines for their communities. It often leaves neighbors searching for answers about the futures of their communities. … Those in the data center industry argue the NDAs serve a particular purpose: ensuring that their competitors aren’t able to access information about their strategies and planned projects before they’re announced. And NDAs are common in many types of economic development deals aside from data centers. But as the facilities have spread into suburbs and farmland, they’ve drawn pushback from dozens of communities concerned by how they could upend daily life.”
Such concerns include inflated electricity prices, water shortages, and air pollution. We would add the dangerous strain on power grids and substantial environmental damage. Residents are also less than thrilled about sights and sounds that would spoil their areas’ natural beauty.
Companies say the NDAs are required to protect trade secrets and stay ahead of the competition. Residents are alarmed to be kept in the dark, sometimes until construction is nearly under way. And local officials are caught between a rock and a hard place– They want the economic boost offered by data centers but are uneasy signing away their duty to inform their constituents. Even in the face of freedom of information requests, which is a point stipulated in at least one contract NBC was privy to. But hey, we cannot let the rights of citizens get in the way of progress, can we?
Cynthia Murrell, November 21, 2025


