META and Another PR Content Marketing Play
October 4, 2024
 This write up is the work of a dinobaby. No smart software required.
This write up is the work of a dinobaby. No smart software required.
I worked through a 3,400 word interview in the orange newspaper. “Alice Newton-Rex: WhatsApp Makes People Feel Confident to Be Themselves: The Messaging Platform’s Director of Product Discusses Privacy Issues, AI and New Features for the App’s 2bn Users” contains a number of interesting statements. The write up is behind the Financial Times’s paywall, but it is worth subscribing if you are monitoring what Meta (the Zuck) is planning to do with regard to E2EE or end-to-end encrypted messaging. I want to pull out four statements from the WhatsApp professional. My approach will be to present the Meta statements and then pose one question which I thought the interviewer should have asked. After the quotes, I will offer a few observations, primarily focusing on Meta’s apparent “me too” approach to innovation. Telegram’s feature cadence appears to be two to four ahead of Meta’s own efforts.
A WhatsApp user is throwing big, soft, fluffy snowballs at the company. Everyone is impressed. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Good enough.
Okay, let’s look at the quotes which I will color blue. My questions will be in black.
Meta Statement 1: The value of end-to-end encryption.
We think that end-to-end encryption is one of the best technologies for keeping people safe online. It makes people feel confident to be themselves, just like they would in a real-life conversation.
What data does Meta have to back up this “we think” assertion?
Meta Statement 2: Privacy
Privacy has always been at the core of WhatsApp. We have tons of other features that ensure people’s privacy, like disappearing messages, which we launched a few years ago. There’s also chat lock, which enables you to hide any particular conversation behind a PIN so it doesn’t appear in your main chat list.
Always? (That means that privacy is the foundation of WhatsApp in a categorically affirmative way.) What do you mean by “always”?
Meta Statement 3:
… we work to prevent abuse on WhatsApp. There are three main ways that we do this. The first is to design the product up front to prevent abuse, by limiting your ability to discover new people on WhatsApp and limiting the possibility of going viral. Second, we use the signals we have to detect abuse and ban bad accounts — scammers, spammers or fake ones. And last, we work with third parties, like law enforcement or fact-checkers, on misinformation to make sure that the app is healthy.
What data can you present to back up these statements about what Meta does to prevent abuse?
Meta Statement 4:
if we are forced under the Online Safety Act to break encryption, we wouldn’t be willing to do it — and that continues to be our position.
Is this position tenable in light of France’s action against Pavel Durov, the founder of Telegram, and the financial and legal penalties nation states can are are imposing on Meta?
Observations:
- Just like Mr. Zuck’s cosmetic and physical make over, these statements describe a WhatsApp which is out of step with the firm’s historical behavior.
- The changes in WhatsApp appear to be emulation of some Telegram innovations but with a two to three year time lag. I wonder if Meta views Telegram as a live test of certain features and functions.
- The responsiveness of Meta to lawful requests has, based on what I have heard from my limited number of contacts, has been underwhelming. Cooperation is something in which Meta requires some additional investment and incentivization of Meta employees interacting with government personnel.
Net net: A fairly high profile PR and content marketing play. FT is into kid glove leather interviews and throwing big soft Nerf balls, it seems.
Stephen E Arnold, October 4, 2024
AI Maybe Should Not Be Accurate, Correct, or Reliable?
September 26, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Okay, AI does not hallucinate. “AI” — whatever that means — does output incorrect, false, made up, and possibly problematic answers. The buzzword “hallucinate” was cooked up by experts in artificial intelligence who do whatever they can to avoid talking about probabilities, human biases migrated into algorithms, and fiddling with the knobs and dials in the computational wonderland of an AI system like Google’s, OpenAI’s, et al. Even the book Why Machines Learn: The Elegant Math Behind Modern AI ends up tangled in math and jargon which may befuddle readers who stopped taking math after high school algebra or who has never thought about Orthogonal matrices.
The Next Web’s “AI Doesn’t Hallucinate — Why Attributing Human Traits to Tech Is Users’ Biggest Pitfall” is an interesting write up. On one hand, it probably captures the attitude of those who just love that AI goodness by blaming humans for anthropomorphizing smart software. On the other hand, the AI systems with which I have interacted output content that is wrong or wonky. I admit that I ask the systems to which I have access for information on topics about which I have some knowledge. Keep in mind that I am an 80 year old dinobaby, and I view “knowledge” as something that comes from bright people working of projects, reading relevant books and articles, and conference presentations or meeting with subjects far from the best exercise leggings or how to get a Web page to the top of a Google results list.
Let’s look at two of the points in the article which caught my attention.
First, consider this passage which is a quote from and AI expert:
“Luckily, it’s not a very widespread problem. It only happens between 2% to maybe 10% of the time at the high end. But still, it can be very dangerous in a business environment. Imagine asking an AI system to diagnose a patient or land an aeroplane,” says Amr Awadallah, an AI expert who’s set to give a talk at VDS2024 on How Gen-AI is Transforming Business & Avoiding the Pitfalls.
Where does the 2 percent to 10 percent number come from? What methods were used to determine that content was off the mark? What was the sample size? Has bad output been tracked longitudinally for the tested systems? Ah, so many questions and zero answers. My take is that the jargon “hallucination” is coming back to bite AI experts on the ankle.
Second, what’s the fix? Not surprisingly, the way out of the problem is to rename “hallucination” to “confabulation”. That’s helpful. Here’s the passage I circled:
“It’s really attributing more to the AI than it is. It’s not thinking in the same way we’re thinking. All it’s doing is trying to predict what the next word should be given all the previous words that have been said,” Awadallah explains. If he had to give this occurrence a name, he would call it a ‘confabulation.’ Confabulations are essentially the addition of words or sentences that fill in the blanks in a way that makes the information look credible, even if it’s incorrect. “[AI models are] highly incentivized to answer any question. It doesn’t want to tell you, ‘I don’t know’,” says Awadallah.
Third, let’s not forget that the problem rests with the users, the personifies, the people who own French bulldogs and talk to them as though they were the favorite in a large family. Here’s the passage:
The danger here is that while some confabulations are easy to detect because they border on the absurd, most of the time an AI will present information that is very believable. And the more we begin to rely on AI to help us speed up productivity, the more we may take their seemingly believable responses at face value. This means companies need to be vigilant about including human oversight for every task an AI completes, dedicating more and not less time and resources.
The ending of the article is a remarkable statement; to wit:
As we edge closer and closer to eliminating AI confabulations, an interesting question to consider is, do we actually want AI to be factual and correct 100% of the time? Could limiting their responses also limit our ability to use them for creative tasks?
Let me answer the question: Yes, outputs should be presented and possibly scored; for example, 90 percent probable that the information is verifiable. Maybe emojis will work? Wow.
Stephen E Arnold, September 26, 2024
AI Automation Has a Benefit … for Some
September 26, 2024
Humanity’s progress runs parallel to advancing technology. As technology advances, aspects of human society and culture are rendered obsolete and it is replaced with new things. Job automation is a huge part of this; past example are the Industrial Revolution and the implementation of computers. AI algorithms are set to make another part of the labor force defunct, but the BBC claims that might be beneficial to workers: “Klarna: AI Lets Us Cut Thousands Of Jobs-But Pay More.”
Klarna is a fintech company that provides online financial services and is described as a “buy now, pay later” company. Klarna plans to use AI to automate the majority of its workforce. The company’s leaders already canned 1200 employees and they plan to fire another 2000 as AI marketing and customer service is implemented. That leaves Klarna with a grand total of 1800 employees who will be paid more.
Klarna’s CEO Sebastian Siematkowski is putting a positive spin on cutting jobs by saying the remaining employees will receive larger salaries. While Siematkowski sees the benefits of AI, he does warn about AI’s downside and advises the government to do something. He said:
“ ‘I think politicians already today should consider whether there are other alternatives of how they could support people that may be effective,’ he told the Today programme, on BBC Radio 4.
He said it was “too simplistic” to simply say new jobs would be created in the future.
‘I mean, maybe you can become an influencer, but it’s hard to do so if you are 55-years-old,’ he said.”
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) predicts that 40% of all jobs will worsen in “overall equality” due to AI. As Klarna reduces its staff, the company will enter what is called “natural attrition” aka a hiring freeze. The remaining workforce will have bigger workloads. Siematkowski claims AI will eventually reduce those workloads.
Will that really happen? Maybe?
Will the remaining workers receive a pay raise or will that money go straight to the leaders’ pockets? Probably.
Whitney Grace, September 26, 2024
But What about the Flip Side of Smart Software Swaying Opinion
September 20, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
The Silicon Valley “fight of the century” might be back on. I think I heard, “Let’s scrap” buzzing in the background when I read “Musk Has Turned Twitter into Hyper-Partisan Hobby Horse, Says Nick Clegg.” Here in Harrod’s Creek, Kentucky, them is fightin’ words. When they are delivered by a British luminary educated at Westminster School before going on to study at the University of Cambridge, the pronouncement is particularly grating on certain sensitive technology super heroes.
The Silicon Valley Scrap is ramping up. One one digital horse is the Zuck. On the other steed is Musk. When the two titans collide, who will emerge as the victor? How about the PR and marketing professionals working for each of the possible chevaliers? Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Good enough.
The write up in the Telegraph (a British newspaper which uses a paywall to discourage the riff raff from reading its objective “real news” stories reports:
Sir Nick, who is now head of global affairs for Facebook-owner Meta, said Mr Musk’s platform, which is now known as X, was used by a tiny group of elite people to “yell at each other” about politics. By contrast, Facebook and Instagram had deprioritized news and politics because people did not want to read it, he said.
Of course, Cambridge University graduates who have studied at the home of the Golden Gophers and the (where is it again?) College of Europe would not “yell.” How plebeian! How nouveau riche! My, my, how déclassé.
The Telegraph reports without a hint of sarcasm:
Meta launched a rival service last year called Threads, but has said it will promote subjects such as sports above news and politics in feeds. Sir Nick, who will next week face a Senate committee about tech companies’ role in elections, said that social media has very little impact on voters’ choices. “People tend to somewhat exaggerate the role that technology plays in how people vote and political behavior,” he said.
As a graduate of a loser school, I wish to humbly direct Sir Richard’s attention to “AI Chatbots Might Be Better at Swaying Conspiracy Theorists Than Humans.” The main idea of the write up of a research project is that:
Experiments in which an AI chatbot engaged in conversations with people who believed at least one conspiracy theory showed that the interaction significantly reduced the strength of those beliefs, even two months later. The secret to its success: the chatbot, with its access to vast amounts of information across an enormous range of topics, could precisely tailor its counterarguments to each individual.
Keeping in mind that I am not the type of person the University of Europe or Golden Gopher U. wants on its campus, I would ask, “Wouldn’t smart software work to increase the power of bad actors or company owners who use AI chatbots to hold opinions promoted by the high-technology companies. If so, Mr. Clegg’s description of X.com as a hobby horse would apply to Sir Richard’s boss, Mark Zuckerberg (aka the Zuck). Surely social media and smart software are able to slice, dice, chop, and cut in multiple directions. Wouldn’t a filter tweaked a certain way provide a powerful tool to define “reality” and cause some users to ramp up their interest in a topic? Could these platforms with a digital finger on the filter controls make some people roll over, pat their tummies, and believe something that the high technology “leadership” wants?
Which of these outstanding, ethical high-technology social media platforms will win a dust up in Silicon Valley? How much will Ticketmaster charge for a ring-side seat? What other pronouncements will the court jesters for these two highly-regarded companies say?
Stephen E Arnold, September 20, 2024
Too Bad Google and OpenAI. Perplexity Is a Game Changer, Says Web Pro News!
September 10, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
I have tested a number of smart software systems. I can say, based on my personal experience, none is particularly suited to my information needs. Keep in mind that I am a dinobaby, more at home in a research library or the now-forgotten Dialog command line. ss cc=7900, thank you very much.
I worked through the write up “Why Perplexity AI Is (Way) Better Than Google: A Deep Dive into the Future of Search.” The phrase “Deep Dive’ reminded me of a less-than-overwhelming search service called Deepdyve. (I just checked and, much to my surprise, the for-fee service is online at https://www.deepdyve.com/. Kudos, Deepdyve, which someone told me was a tire kicker or maybe more with the Snorkle system. (I could look it up using a smart software system, but performance is crappy today, and I don’t want to get distracted from the Web Pro News pronouncement. But that smart software output requires a lot of friction; that is, verifying that the outputs are accurate.)
A dinobaby (the author of this blog post) works in a library. Thanks, MSFT Copilot, good enough.
Here’s the subtitle to the article. Its verbosity smacks of that good old and mostly useless search engine optimization tinkering:
Perplexity AI is not just a new contender; it’s a game-changer that could very well dethrone Google in the years to come. But what exactly makes Perplexity AI better than Google? Let’s explore the…
No, I didn’t truncate the subtitle. That’s it.
The write up explains what differentiates Perplexity from the other smart software, question-answering marvels. Here’s a list:
- Speed and Precision at Its Core
- Specialized Search Experience for Enterprise Needs
- Tailored Results and User Interaction
- Innovations in Data Privacy
- Ad-Free Experience: A Breath of Fresh Air
- Standardized Interface and High Accuracy
- The Potential to Revolutionize Search
In my experience, I am not sure about the speed of Perplexity or any smart search and retrieval system. Speed must be compared to something. I can obtain results from my installation of Everything search pretty darned quick. None of the cloud search solutions comes close. My Mistal installation grunts and sweats on a corpus of 550 patent documents. How about some benchmarks, WebProNews?
Precision means that the query returns documents matching a query. There is a formula (which is okay as formulae go) which is, as I recall, Relevant retrieved instances divided by All retrieved instances. To calculate this, one must take a bounded corpus, run queries, and develop an understanding of what is in the corpus by reading documents and comparing outputs from test queries. Then one uses another system and repeats the queries, comparing the results. The process can be embellished, particularly by graduate students working on an advanced degree. But something more than generalizations are needed to convince me of anything related to “precision.” Determining precision is impossible when vendors do not disclose sources and make the data sets available. Subjective impressions are okay for messy water lilies, but in the dinobaby world of precision and its sidekick recall, a bit of work is necessary.
The “specialized search experience” means what? To me, I like to think about computational chemists. The interface has to support chemical structures, weird CAS registry numbers, words (mostly ones unknown to a normal human), and other assorted identifiers. As far as I know, none of the smart software I have examined does this for computational chemists or most of the other “specialized” experiences engineers, mathematicians, or physicists, among others, use in their routine work processes. I simply don’t know what Web Pro News wants me to understand. I am baffled, a normal condition for dinobabies.
I like the idea of tailored results. That’s what Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube try to deliver in order to increase stickiness. I think in terms of citations to relevant documents relevant to my query. I don’t like smart software which tries to predict what I want or need. I determine that based on the information I obtain, read, and write down in a notebook. Web Pro News and I are not on the same page in my paper notebook. Dinobabies are a pain, aren’t they?
I like the idea of “data privacy.” However, I need evidence that Perplexity’s innovations actually work. No data, no trust: Is that difficult for a younger person to understand?
The standardized interface makes life easy for the vendor. Think about the computational chemist. The interface must match her specific work processes. A standard interface is likely to be wide of the mark for some enterprise professionals. The phrase “high accuracy” means nothing without one’s knowing the corpus from which the index is constructed. Furthermore the notion of probability means “close enough for horseshoes.” Hallucination refers to outputs from smart software which are wide of the mark. More insidious are errors which cannot be easily identified. A standard interface and accuracy don’t go together like peanut butter and jelly or bread and butter. The interface is separate from the underlying system. The interface might be “accurate” if the term were defined in the write up, but it is not. Therefore, accuracy is like “love,” “mom,” and “ethics.” Anything goes just not for me, however.
The “potential to revolutionize search” is marketing baloney. Search today is more problematic than anytime in my more than half century of work in information retrieval. The only thing “revolutionary” are the ways to monetize users’ belief that the outputs are better, faster, cheaper than other available options. When one thinks about better, faster, and cheaper, I must add the caveat to pick two.
What’s the conclusion to this content marketing essay? Here it is:
As we move further into the digital age, the way we search for information is changing. Perplexity AI represents a significant step forward, offering a faster, more accurate, and more user-centric alternative to traditional search engines like Google. With its advanced AI technologies, ad-free experience, and commitment to data privacy, Perplexity AI is well-positioned to lead the next wave of innovation in search. For enterprise users, in particular, the benefits of Perplexity AI are clear. The platform’s ability to deliver precise, context-aware insights makes it an invaluable tool for research-intensive tasks, while its user-friendly interface and robust privacy measures ensure a seamless and secure search experience. As more organizations recognize the potential of Perplexity AI, we may well see a shift away from Google and towards a new era of search, one that prioritizes speed, precision, and user satisfaction above all else.
I know one thing the stakeholders and backers of the smart software hope that one of the AI players generates tons of cash and dump trucks of profit sharing checks. That day is, I think, lies in the future. Perplexity hopes it will be the winner; hence, content marketing is money well spent. If I were not a dinobaby, I might be excited. So far I am just perplexed.
Stephen E Arnold, September 10, 2024
What are the Real Motives Behind the Zuckerberg Letter?
September 5, 2024
Senior correspondent at Vox Adam Clarke Estes considers the motives behind Mark Zuckerberg’s recent letter to Rep. Jim Jordan. He believes “Mark Zuckerberg’s Letter About Facebook Censorship Is Not What it Seems.” For those who are unfamiliar: The letter presents no new information, but reminds us the Biden administration pressured Facebook to stop the spread of Covid-19 misinformation during the pandemic. Zuckerberg also recalls his company’s effort to hold back stories about Hunter Biden’s laptop after the FBI warned they might be part of a Russian misinformation campaign. Now, he insists, he regrets these actions and vows never to suppress “freedom of speech” due to political pressure again.
Naturally, Republicans embrace the letter as further evidence of wrongdoing by the Biden-Harris administration. Many believe it is evidence Zuckerberg is kissing up to the right, even though he specifies in the missive that his goal is to be apolitical. Estes believes there is something else going on. He writes:
“One theory comes from Peter Kafka at Business Insider: ‘Zuckerberg very carefully gave Jordan just enough to claim a political victory — but without getting Meta in any further trouble while it defends itself against a federal antitrust suit. To be clear, Congress is not behind the antitrust lawsuit. The case, which dates back to 2021, comes from the FTC and 40 states, which say that Facebook illegally crushed competition when it acquired Instagram and WhatsApp, but it must be top of mind for Zuckerberg. In a landmark antitrust case less than a month ago, a federal judge ruled against Google, and called it a monopoly. So antitrust is almost certainly on Zuckerberg’s mind. It’s also possible Zuckerberg was just sick of litigating events that happened years ago and wanted to close the loop on something that has caused his company massive levels of grief. Plus, allegations of censorship have been a distraction from his latest big mission: to build artificial general intelligence.”
So is it coincidence this letter came out during the final weeks of a severely close, high-stakes presidential election? Perhaps. An antitrust ruling like the one against Google could be inconvenient for Meta. Curious readers can navigate to the article for more background and more of Estes reasoning.
Cynthia Murrell, September 5, 2024
Salesforces Disses Microsoft Smart Software
September 4, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
Senior managers can be frisky at times. A good example appears in the Fortune online service write up “Salesforce CEO Marc Benioff Says Microsoft Copilot Has Disappointed Many Customers.” I noted this statement in the article:
Marc Benioff said Microsoft’s Copilot AI hasn’t lived up to the hype…. unimpressive.
The old fish comparison works for smart software it seems. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Good enough just not tastier.
Consider the number of organizations which use Microsoft and its smart software. Will those organizations benefit from “unimpressive” programs and services. What about the US government which might struggle to operate without Microsoft software. What if the US government operates in a way which delivers unimpressive performance? What about companies relying on Microsoft technology? Will these organizations struggle to deliver high-octane performance?
The article reported that the Big Dog of Salesforce opined:
“So many customers are so disappointed in what they bought from Microsoft Copilot because they’re not getting the accuracy and the response that they want,” Benioff said. “Microsoft has disappointed so many customers with AI.”
“Disappointed” — That’s harsh.
True to its rich history of business journalism, the article included a response from Microsoft, a dominant force in enterprise and consumer software (smart or otherwise). I noted this Microsoft comment:
Jared Spataro, Microsoft’s corporate vice president for AI at work, said in a statement to Fortune that the company was “hearing something quite different,” from its customers. The company’s Copilot customers also shot up 60% last quarter and daily users have more than doubled, Spataro added.
From Microsoft’s point of view, this is evidence that Microsoft is delivering high-value smart software. From Salesforce’s point of view, Microsoft is creating customers for Salesforce’s smart software. The problem is that Salesforce is not exactly the same type of software outfit as Salesforce. Nevertheless, the write up included this suggestive comment from the Big Dog of Salesforce:
“With our new Agentforce platform, we’re going to make a quantum leap for AI,” he said.
I like the use of the word “quantum.” It suggests uncertainty to me. I remain a bit careful when it comes to discussions of “to be” software. Marketing-type comments are far easier to create than a functional, reliable, and understandable system infused with smart software.
But PR and marketing are one thing. Software which does not hallucinate or output information that cannot be verified given an organization’s resources is different. Who cares? That’s a good question. Stakeholders, those harmed by AI outputs, and unemployed workers replaced by more “efficient” systems maybe?
Content marketing, sales hyperbole, and PR — The common currency of artificial intelligence makes life interesting.
Stephen E Arnold, September 4, 2024
Cyber Security Outfit Wants Its Competition to Be Better Fellow Travelers
August 21, 2024
![green-dino_thumb_thumb_thumb_thumb_t[2] green-dino_thumb_thumb_thumb_thumb_t[2]](https://arnoldit.com/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/green-dino_thumb_thumb_thumb_thumb_t2_thumb-1.gif) This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
I read a write up which contains some lingo that is not typical Madison Avenue sales speak. The sort of odd orange newspaper published “CrowdStrike Hits Out at Rivals’ Shady Attacks after Global IT Outage.” [This is a paywalled story, gentle reader. Gone are the days when the orange newspaper was handed out in Midtown Manhattan.] CrowdStrike is a company with interesting origins. The firm has become a player in the cyber security market, and it has been remarkably successful. Microsoft — definitely a Grade A outfit focused on making system administrators’ live as calm as Lake Paseco on summer morning — allowed CrowdStrike to interact with the most secure component of its software.
What does the leader of CrowdStrike reveal? Let’s take a quick look at a point or two.
First, I noted this passage from the write up which seems a bit a proactive tactic to make sure those affected by the tiny misstep know that software is not perfect. I mean who knew?
CrowdStrike’s president hit out at “shady” efforts by its cyber security rivals to scare its customers and steal market share in the month since its botched software update sparked a global IT outage. Michael Sentonas told the Financial Times that attempts by competitors to use the July 19 disruption to promote their own products were “misguided”.
I am not sure what misguided means, but I think the idea is that competitors should not try to surf on the little ripples the CrowdStrike misstep caused. A few airline passengers were inconvenienced, sure. But that happens anyway. The people in hospitals whose surgeries were affected seem to be mostly okay in a statistical sense. And those interrupted financial transactions. No big deal. The market is chugging along.
Cyber vendors are ready and eager to help those with a problematic and possibly dangerous vehicle. Thanks, MSFT Copilot. Are you hands full today?
I also circled this passage:
SentinelOne chief executive Tomer Weingarten said the global shutdown was the result of “bad design decisions” and “risky architecture” at CrowdStrike, according to trade magazine CRN. Alex Stamos, SentinelOne’s chief information security officer, warned in a post on LinkedIn it was “dangerous” for CrowdStrike “to claim that any security product could have caused this kind of global outage”.
Yep, dangerous. Other vendors’ software are unlikely to create a CrowdStrike problem. I like this type of assertion. Also, I find the ambulance-chasing approach to closing deals and boosting revenue a normal part of some companies’ marketing. I think one outfit made FED or fear, uncertainty, and doubt a useful wrench in the firm’s deal-closing guide to hitting a sales target. As a dinobaby, I could be hallucinating like some of the smart software and the even smarter top dogs in cyber security companies.
I have to include this passage from the orange outfit’s write up:
Sentonas [a big dog at CrowdStrike], who this month went to Las Vegas to accept the Pwnie Award for Epic Fail at the 2024 security conference Def Con, dismissed fears that CrowdStrike’s market dominance would suffer long-term damage. “I am absolutely sure that we will become a much stronger organization on the back of something that should never have happened,” he said. “A lot of [customers] are saying, actually, you’re going to be the most battle-tested security product in the industry.”
The Def Con crowd was making fun of CrowdStrike for is inconsequential misstep. I assume CrowdStrike’s leadership realizes that the award is like a having the “old” Mad Magazine devote a cover to a topic.
My view is that [a] the incident will be forgotten. SolarWinds seems to be fading as an issue in the courts and in some experts’ List of Things to Worry About. [b] Microsoft and CrowdStrike can make marketing hay by pointing out that each company has addressed the “issue.” Life will be better going forward. And, [c] Competitors will have to work overtime to cope with a sales retention tactic more powerful than any PowerPoint or PR campaign — discounts, price cuts, and free upgrades to AI-infused systems.
But what about that headline? Will cyber security marketing firms change their sales lingo and tell the truth? Can one fill the tank of a hydrogen-powered vehicle in Eastern Kentucky?
PS. Buying cyber security, real-time alerts, and other gizmos allow an organization to think, “We are secure, right?”
Stephen E Arnold, August 21, 2024
Deep Fake Service?
August 16, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb dinobaby. No smart software required.
What sets DeepLive apart is that one needs only a single image and the video of the person whose face you want to replace. The technology — assuming it is functioning as marketed — makes it clear that swapping faces on videos can be done. Will the technology derail often-controversial facial recognition systems?
The Web site provides testimonials and some examples of DeepLive in action.
The company says:
Deep Live Cam is an open-source tool for real-time face swapping and one-click video deepfakes. It can replace faces in videos or images using a single photo, ideal for video production, animation, and various creative projects.
The software is available as open source. The developers says that it includes “ethical safeguards.” But just in case these don’t work, DeepLive posts this message on its Web site:
Built-in checks prevent processing of inappropriate content, ensuring legal and ethical use.
The software has a couple of drawbacks:
- It is not clear if this particular code base is on an open source repository. There are a number of Deep Live this and thats.
- There is no active Web page link to the “Get Started” button
- There is minimal information about the “owner” of the software.
Other than that DeepLive is a good example of a deep fake. (An interesting discussion appears in HackerNews and Ars Technica.) If the system is stable and speedy, AI-enabled tools to create content objects for a purpose has taken a step forward. Bad actors are probably going to take note and give the system a spin.
Stephen E Arnold, August 16, 2024
AI Research: A New and Slippery Cost Center for the Google
August 7, 2024
 This essay is the work of a dumb humanoid. No smart software required.
This essay is the work of a dumb humanoid. No smart software required.
A week or so ago, I read “Scaling Exponents Across Parameterizations and Optimizers.” The write up made crystal clear that Google’s DeepMind can cook up a test, throw bodies at it, and generate a bit of “gray” literature. The objective, in my opinion, was three-fold. [1] The paper makes clear that DeepMind is thinking about its smart software’s weaknesses and wants to figure out what to do about them. And [2] DeepMind wants to keep up the flow of PR – Marketing which says, “We are really the Big Dogs in this stuff. Good luck catching up with the DeepMind deep researchers.” Note: The third item appears after the numbers.
I think the paper reveals a third and unintended consequence. This issue is made more tangible by an entity named 152334H and captured in “Calculating the Cost of a Google DeepMind Paper.” (Oh, 152334 is a deep blue black color if anyone cares.)
That write up presents calculations supporting this assertion:
How to burn US$10,000,000 on an arXiv preprint
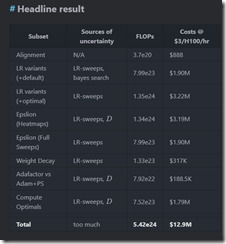
The write up included this table presenting the costs to replicate what the xx Googlers and DeepMinders did to produce the ArXiv gray paper:
Notice, please, that the estimate is nearly $13 million. Anyone want to verify the Google results? What am I hearing? Crickets.
The gray paper’s 11 authors had to run the draft by review leadership and a lawyer or two. Once okayed, the document was converted to the arXiv format, and we the findings to improve our understanding of how much work goes into the achievements of the quantumly supreme Google.
Thijs number of $12 million and change brings me to item [3]. The paper illustrates why Google has a tough time controlling its costs. The paper is not “marketing,” because it is R&D. Some of the expense can be shuffled around. But in my book, the research is overhead, but it is not counted like the costs of cubicles for administrative assistants. It is science; it is a cost of doing business. Suck it up, you buttercups, in accounting.
The write up illustrates why Google needs as much money as it can possibly grab. These costs which are not really nice, tidy costs have to be covered. With more than 150,000 people working on projects, the costs of “gray” papers is a trigger for more costs. The compute time has to be paid for. Hello, cloud customers. The “thinking time” has to be paid for because coming up with great research is open ended and may take weeks, months, or years. One could not rush Einstein. One cannot rush Google wizards in the AI realm either.
The point of this blog post is to create a bit of sympathy for the professionals in Google’s accounting department. Those folks have a tough job figuring out how to cut costs. One cannot prevent 11 people from burning through computer time. The costs just hockey stick. Consequently the quantumly supreme professionals involved in Google cost control look for simpler, more comprehensible ways to generate sufficient cash to cover what are essentially “surprise” costs. These tools include magic wand behavior over payments to creators, smart commission tables to compensate advertising partners, and demands for more efficiency from Googlers who are not thinking big thoughts about big AI topics.
Net net: Have some awareness of how tough it is to be quantumly supreme. One has to keep the PR and Marketing messaging on track. One has to notch breakthroughs, insights, and innovations. What about that glue on the pizza thing? Answer: What?
Stephen E Arnold, August 7, 2024